"The action can't be completed because the folder or a file in it is open in another program Close the folder or file and try again."
git bash: "Unlink of file 'lib/ojdbc8.jar' failed. Should I try again? (y/n)"
So follow the steps below to resolve the issue:
1. From the Windows Start menu, open "Resource Monitor" program.
2. Choose the "CPU" tab.
3. Enter the file name or folder name to "Search Handles" box.
4. Choose from the result to kill (End Process) the programs which access to the files or folders.
Now you can modify, move or delete the files or folders as normal.
:))
This is where I noted some things when I working with Operating Systems, Virtualization, Containers, Databases, Programming Languages, Frameworks, and Development Tools to reuse and for time-saving later.
Search
Total Pageviews
Categories
Linux
(8)
Windows
(5)
Container
(4)
Development
(4)
Database
(3)
Docker
(3)
Mac OS
(3)
QuickStart
(3)
Ubuntu
(3)
AWS
(1)
Fedora
(1)
FreeBSD
(1)
Git
(1)
Java
(1)
MyBatis
(1)
Oracle Linux
(1)
Spring Boot
(1)
Unix
(1)
VMware
(1)
Virtualization
(1)
kdevtmpfsi
(1)
kinsing
(1)
Featured Post
Your container's CPU usage is more than 100%, "kdevtmpfsi" the cryptomining malware is running | So how to resolve
How to resolve when "kdevtmpfsi" the crypto-mining malware is running and taking all CPU load of your server (container). One d...

Wednesday, July 3, 2019
Saturday, January 26, 2019
QuickStart: The fastest and easiest way to run an Instance of Oracle Database on Mac OS
Run Oracle Database on your Mac.
-> Via Docker and Oracle Database Enterprise Edition Image with few steps in minutes.
Install Docker CE for Mac and log in to Docker Hub.
- Register a Docker ID if you don't have.
- Skip this step if Docker already installed on your Mac and you already logged in Docker Hub.
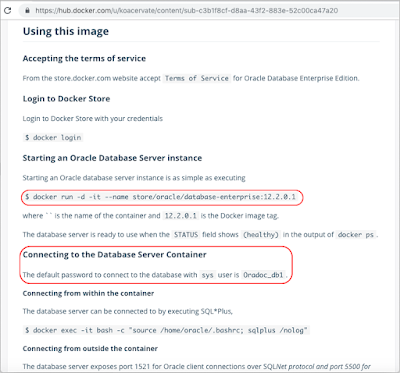
- Run the command below to starting an Oracle Database Server Instance as a Docker container named "Oracle-DB" and mapping port 1521 from the container to port 1521 on your Docker host (your Mac). This will take you a few minutes to download the image and Starting the container.
Pull and run Oracle Database Enterprise Edition Image from Docker Hub.
- Search for "Oracle Database Enterprise Edition" in Docker Hub and Checkout the document for more details.- Run the command below to starting an Oracle Database Server Instance as a Docker container named "Oracle-DB" and mapping port 1521 from the container to port 1521 on your Docker host (your Mac). This will take you a few minutes to download the image and Starting the container.
docker run -d -it --name Oracle-DB -p 1521:1521/tcp store/oracle/database-enterprise:12.2.0.1
- Ok, So now you already have an instance of Oracle Database server in your Mac for testing or development. When you don't want the instance running and saving your Mac performance, you can stop the container or want to start the instance again as below:
- If your project is done and you don't want to use the instance any more, you should stop the container and delete the image as below:
- And remove unused volume:
docker volume prune
Error Notes: When you connect from Oracle SQL Developer Tool to the Oracle Database Server Instance, if you get a message "Status: Failure -Test failed: IO Error: Got minus one from a read call" or "Status: Failure -Test failed: Listener refused the connection with the following error:
ORA-12505, TNS: listener does not currently know of SID given in connect descriptor" -> So please wait in moments, the instance is preparing in the container, you can connect success very soon after that, don't worry :). Good luck and fun.References:
- https://docs.docker.com
- https://hub.docker.com/_/oracle-database-enterprise-edition?tab=resources
Saturday, July 1, 2017
How to Install and use the Linux Ubuntu Bash Shell on Windows 10
Ubuntu-based Bash shell that can run Linux software directly on Windows. Ofcourse, only softwares based on Bash Shel. This isn’t a virtual machine, a container, or Linux software compiled for Windows (like Cygwin).
This is the version of Windows 10 I'm using to install Linux Ubuntu Bash Shell.
Please make sure your Windows 10 is up to date.
Open the Settings app and head to Update & Security > For Developers. Activate the “Developer Mode” switch here to enable Developer Mode.
Next, open the Control Panel, click “Programs,” and click “Turn Windows Features On or Off” under Programs and Features. Enable the “Windows Subsystem for Linux (Beta)” option in the list here and click “OK.”
After you do, you’ll be prompted to reboot your computer. Click “Restart Now” to reboot your computer and Windows 10 will install the new feature.
After your computer restarts, click the Start button (or press the Windows key), type “bash”, and press “Enter.”
You’ll be prompted to accept the terms of service. You’ll be asked to create a user account and password for use in the Bash environment.
Open your Start menu and search for “bash” or “Ubuntu.” You’ll see a “Bash on Ubuntu on Windows” application.
So now you can using your Linux favorite commands and install bash tools on Windows 10 as you familiar on your Linux.
Please refer to get more info about Linux Ubuntu Bash Shell on Windows 10.
This is the version of Windows 10 I'm using to install Linux Ubuntu Bash Shell.
Please make sure your Windows 10 is up to date.
Open the Settings app and head to Update & Security > For Developers. Activate the “Developer Mode” switch here to enable Developer Mode.
Next, open the Control Panel, click “Programs,” and click “Turn Windows Features On or Off” under Programs and Features. Enable the “Windows Subsystem for Linux (Beta)” option in the list here and click “OK.”
After you do, you’ll be prompted to reboot your computer. Click “Restart Now” to reboot your computer and Windows 10 will install the new feature.
After your computer restarts, click the Start button (or press the Windows key), type “bash”, and press “Enter.”
Open your Start menu and search for “bash” or “Ubuntu.” You’ll see a “Bash on Ubuntu on Windows” application.
Please refer to get more info about Linux Ubuntu Bash Shell on Windows 10.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)